Friday September 16 2022
The Complete Guide to Multivitamins
Written by:
The Prym Health Team
6 minute read
Contents:
- Introduction
- Water soluble vs fat soluble multivitamins
- What do multivitamins contain?
- Who should take multivitamins?
- What is the best time to take multivitamin?
- Summary
- Sources
Introduction
Multivitamins are one of the most common supplements used in the world, and their popularity is rising day by day. Some people use multivitamins to improve their health, and others use them to mitigate the risks of developing chronic diseases. Multivitamin supplements contain a blend of different vitamins and minerals that are essential for our body to work properly.
To maintain overall balance and stability in the body, we need 15 minerals and 13 vitamins. These chemical components may be hormones or enzymes that are used to keep our organs functioning properly. These nutrients are also essential for carrying out processes such as growth development, maintenance and reproduction.
Interestingly there is no international standard to define multivitamins because the nutrient composition varies with product to product and brand to brand. These supplements are readily available in supermarkets, health stores, pharmacies and online marketplaces.
Let’s delve deeper into the world of multivitamins and their importance on the human body.
Water Soluble vs Fat Soluble Multivitamins
There are two main categories of multivitamins, i.e., water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins.
Water soluble vitamins: these vitamins are dissolved in water, and they are instantly available to our tissues for immediate use. Unlike fat-soluble vitamins, water-soluble ones do not get stored in the body, and we need to replenish them regularly through our diet. Instead of keeping the excess vitamins, our body excretes water-soluble vitamins in urine to save the body from toxicity.
Fat soluble vitamins: these need to be dissolved in fat globules and reach the small intestine to enter the bloodstream. Excess fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the liver and the adipose tissues so that they can be used in future. (1)
What Do Multivitamins Contain?
Multivitamins are composed of the essential minerals and vitamins which all play a different role in maintaining the health of the human body. We’ve included a list of the most common below.
Retinol
Retinol is also known as vitamin A and it has some key roles to play. It boosts the production of red and white blood cells so that our immune system can work properly. Vitamin A is also essential for rebuilding bones and regulating the growth and division of the cell, thereby reducing the risk of cancer. It is also used to cure inflammatory skin conditions like acne and eczema. Vitamin A deficiency is quite common in developing countries and causes night blindness and sometimes complete blindness as well (2). It also increases the susceptibility to infectious diseases. Adults need no more than 700 micrograms of retinol for proper functioning. Foods such as salmon, cheddar and hard-boiled eggs are found to be a natural sources of high Vitamin A levels. It is also commonly found in many skin care products due to its effects on the skin, including exfoliating the skin and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. However, it is important to note that more than 1500 micrograms of Vitamin A over a long period can cause toxicity and may lead to nausea, disease, skin irritation, and even death.
Thiamin
Thiamin, or Vitamin B1 as it’s also known, is a vital component for our overall health and bodily functions. Overall it is considered as a safe vitamin however taken in large doses can lead to an upset stomach. The recommended dosage for adult men is 1.2 milligrams and 1.1 milligrams for adult women. However, a supplement is not always required to reach these levels as you can obtain from Thiamin-rich foods such as salmon, flax seeds, green beans, brown rice and tofu. A balanced diet is the first step to optimum health.
Riboflavin
Riboflavin, otherwise known as Vitamin B2, is a water-soluble vitamin which helps convert food into energy. It also helps maximum absorption of iron into our intestine and allows the optimal growth of skin, hair and muscle. Riboflavin is also important for the functioning of our brain. As the body does not store excess amounts of riboflavin, a deficiency can occur and this is an issue as it can lead to problems such as mouth ulcers, cracked lips, sensitivity to light and inflammation of the tongue (3). An average adult needs 1.3 milligrams of riboflavin daily, which can also be obtained through foods such as plain yoghurt or milk.
Niacin
As with the previous vitamins from the B-Group, Niacin, or Vitamin B3, is essential in helping the body convert food into energy. Alongside this, reaching the recommended amount can help the body maintain healthy hair, skin and sufficient red blood cells which carry oxygen from our lungs to the rest of the body. Niacin is also crucial for our nervous system and liver as it can reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and high cholesterol. Furthermore, extreme deficiency of Vitamin B3 causes pellagra leading to dermatitis or dementia. Adult males need approximately 16 milligrams of niacin whilst adult females need 13milligrams. Natural sources such as brown rice, grilled chicken breast and eggs provide a good level of the vitamin.
Pantothenic Acid
Along with being essential for food metabolism, Pantothenic Acid or Vitamin B5 is also important as it synthesizes neurotransmitters, red blood cells and steroid hormones. With the recommended dosage being only 5 milligrams for adults, a deficiency is rare. However, if you do lack the vitamin, it can lead to fatigue, insomnia, depression and irritability. Natural sources of Vitamin B5 include sunflower seeds, chicken breast and mushrooms.
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is also known as pyridoxal or pyridoxine. This vitamin is vital for better mood, appetite and sleep. Vitamin B6 is directly related to the production of serotonin, an important neurotransmitter which plays key functions in the body. B6 also helps in manufacturing red blood cells and thyroid hormones essential for our cognition and immune system. Adults need 1.3 milligrams of Vitamin B6 daily and can be found in foods such as chickpeas and bananas. However, taking excess Vitamin B6 for an extended time span can cause loss of control over body movements and painful skin lesions.
Biotin
Biotin, also known as Vitamin B7, plays a key role in the food metabolism of our body. Metabolic activity is required to carry out all essential physiological functions. Deficiency of Vitamin B7 is quite rare however an adult need 30 micrograms per day to maintain the appropriate level. Vitamin B7 can be obtained through foods such as liver, fish, seeds and nuts.
Vitamin B12
B12 plays a crucial role in the metabolism of amino acids and fatty acids. Not only this, but it also works to protect the nerves, which is why it can help in reducing the risk of diseases such as Alzheimer’s. A deficiency of the vitamin is more prevalent amongst the elderly. To maintain a healthy balance, 2.4 micrograms of Vitamin B12 per day is recommended and this can be obtained through foods such as milk, fish and meat.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is one of the most popular and most important supplements of all. This is because it plays a key role in the growth, development and repair of all body tissues. Not only this, but it can also help in producing collagen, which is an essential compound for rejuvenating skin. More commonly, Vitamin C is associated with helping strengthen the immune system allowing the body to fight off infections and illness. A deficiency in Vitamin C can be fatal as it may lead to severe bleeding along with other issues such as joint pain, hair and tooth loss. The recommended dosage of Vitamin C is 90 milligrams per day, however taking the vitamin in excess of this can cause abdominal cramps and nausea. Fruits, especially citrus, and vegetables are great sources of Vitamin C.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is one of the essential fat-soluble vitamins which is required for calcium metabolism and bone density along with boosting the function of the immune system and the nervous system. Before coming into effect, Vitamin D needs to be activated by UV rays, so a little bit of sunshine every day is required to gain the adequate levels of Vitamin D. Chronic deficiency of the vitamin may cause osteoporosis, especially in women. More than 100 micrograms of Vitamin D per day can be harmful.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a complex of 8 antioxidants that can help reduce the damage caused by free radicals (unstable atoms that damage cells) (4) and maintain cell membrane integrity. In addition, an ample amount of Vitamin E is required for muscle strengthening, balance and coordination. Natural food sources such as sunflower seeds, almonds, peppers and so forth can provide the recommended dosage of 4 milligrams for adult males and 3 milligrams for adult females.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is also fat-soluble vitamin which is required to help the blood clot thus preventing heavy bleeding. Adults need approximately 1 microgram a day of Vitamin K for each kilogram of their body weight. Vitamin K is found in green leafy vegetables and cereal grains and as liver stores excess amounts for future use, it is not necessary to obtain it on a daily basis.
Minerals In Multivitamins
Vitamins are not the only healthy chemical compounds we require. Some minerals are also highly essential for us and we’ve included them below.
Calcium
Calcium is one of the most important macronutrients, which is essential for the development of our teeth and bones. But that’s not all because it also has to play a vital role in nerve signaling, hormone secretion, blood clotting, muscle function and optimising blood pressure. Commonly, calcium is obtained in dairy products however for those who prefer to stay away from animal-based products, green leafy vegetables, white bread and dried fruits are an easily accessible source. With the help of everyday foods, the recommended dosage of 700 milligrams can be reached with ease. Calcium in excess levels of this can however lead to issues such as kidney stones and cardiovascular problems.
Iodine
Iodine is an essential trace mineral as it is a component of thyroid hormones which are essential for maintaining our basal metabolic rate. The recommended dosage is 140 micrograms for an adult and can be found in plant foods such as cereals and grains. Although this level can be easily reached through a balanced diet, too much of it can alter the way the thyroid gland works leading to weight gain amongst other symptoms.
Iron
Iron is used by the body to make hemoglobin, the special protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. A lack of Iron is referred to as Iron Deficiency Amaemia and symptoms of this can include tiredness and lack of energy, shortness of breath, heart palpitations and pale skin. Foods such as red meat, liver and beans can provide the recommended dosage of 8.7 milligrams for adult males and 14.8 milligrams for adult females aged 18-50. Taking iron in excess can lead to complications such as constipation and stomach pain and very high dosages can be fatal.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a key factor in ensuring several parts of the body runs smoothly and this includes the heart, bones, muscles and nerves. Food sources such as spinach, nuts and wholemeal bread can help you reach the recommended dosage of 300 milligrams a day for adult males and 270 milligrams a day for adult females.

Who Should Take Multivitamins?
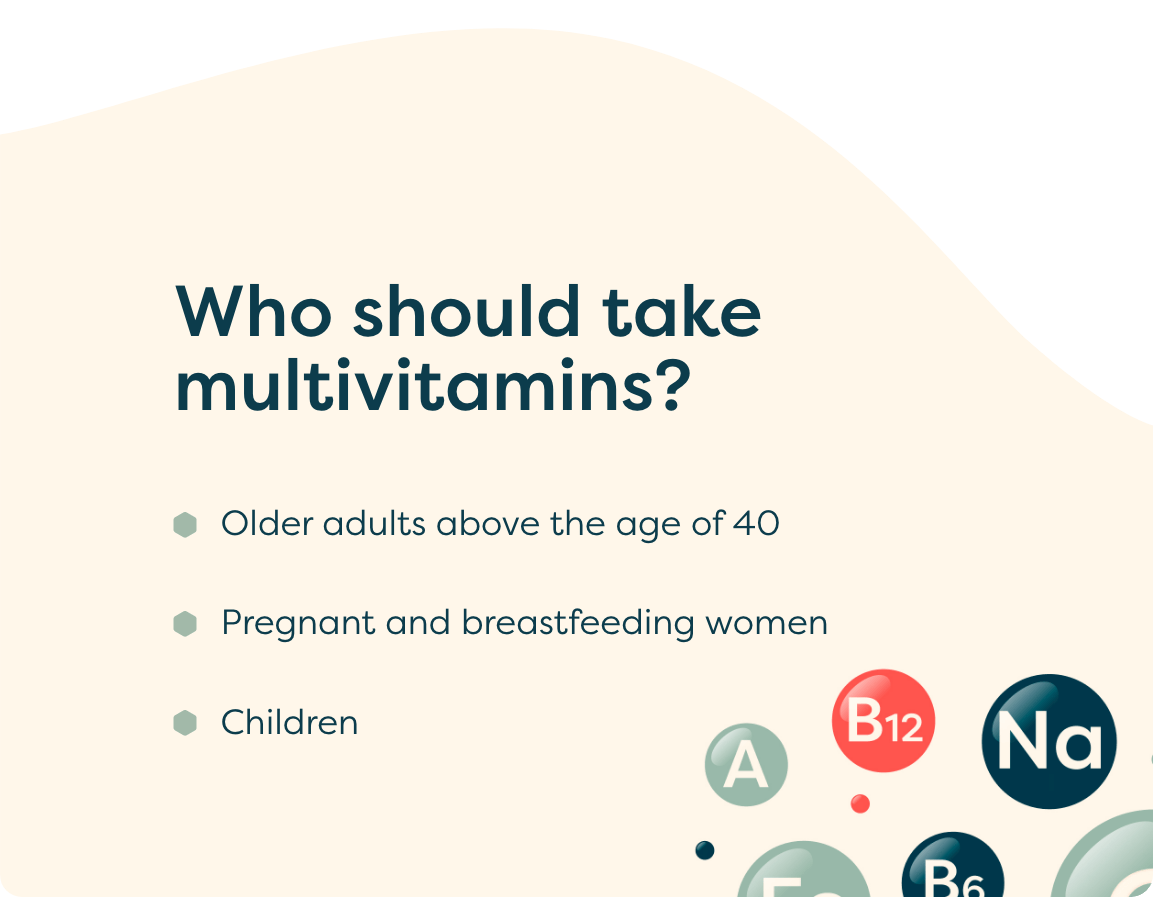
Although the optimum levels of the vitamins and minerals that the human body needs can be obtained through a healthy and balanced diet, there are certain groups of people that may benefit from the use of a multivitamin supplement.
Older adults above the age of 40
As time goes on and we age, the body begins to struggle to absorb and metabolise certain nutrients so supplementing with a multivitamin can counteract this. (5)
Pregnant and breastfeeding women
During pregnancy there is a higher need for folic acid in order to reduce the risk of problems in the baby’s development, especially during the early weeks of pregnancy (6).
Children
Children between the ages of 6 months to 5 years need a significant amount of Vitamin A, C and D for optimum development and growth (7).
Needless to say, you may not fall into one of these categories and if you feel you are unable to obtain the necessary vitamins and minerals through diet due to your lifestyle, a multivitamin supplement may still be beneficial for you.

What is the best time to take multivitamin?
There are no hard rules that dictate when you should take your multivitamins. However, since formulas tend to contain fat-soluble vitamin such as Vitamins A, D, E and K, which dissolve in oil, it is recommended to always take them with a meal.
Because multivitamins often create nutrients that support energy production, it is understandable that many people get into a routine of taking their multivitamin with breakfast. It is a great way to set yourself up for the day and won’t interfere with your sleep.
However, it is important to note that your breakfast should contain some healthy fats, such as avocados, eggs, chia seeds, nuts or oil fish as an example. This way, your body will have the best opportunity to metabolise the nutrients provided by your multivitamin.

Summary
Multivitamin supplements are essential to maintain balance and overall stability for the human body. There are 15 key minerals and 13 vitamins that we require and we are able to obtain these from natural food sources so a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle is most important. However, if you feel you may be deficient in a mineral or vitamin, a multivitamin supplement can be helpful. This is more so true for older adults above the age of 40, pregnant women and children who commonly find themselves deficient in key minerals and vitamins.
So, you may be wondering where you purchase premium multivitamins? As always, here at Prym Health, we bring you the highest quality CBD and nutritional supplements, including a well-balanced chewable multivitamin gummy in a blood orange flavor which can be found here (8). For a limited time, we are offering readers 20% off this supplement with code MV20. Be sure to leave us feedback on hair experience and like our Facebook page and Instagram page for more exclusive offers.

Sources
- https://www.simplysupplements.co.uk/healthylife/general-health/what-are-fat-soluble-vitamins
- https://bjo.bmj.com/content/88/4/583
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/219561#deficiency
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318652
- https://www.nutrition.org.uk/news/2021/a-healthy-immune-system-for-older-adults/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19445414/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/baby/weaning-and-feeding/vitamins-for-children/
- https://prymhealth.com/product/blood-orange-multivitamin/
